In today’s competitive and fast-paced business environment, organizations continuously seek ways to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and improve decision-making. One of the most effective tools for achieving these goals is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). ERP systems have become a cornerstone of modern business, providing comprehensive solutions to integrate and manage core business processes seamlessly.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
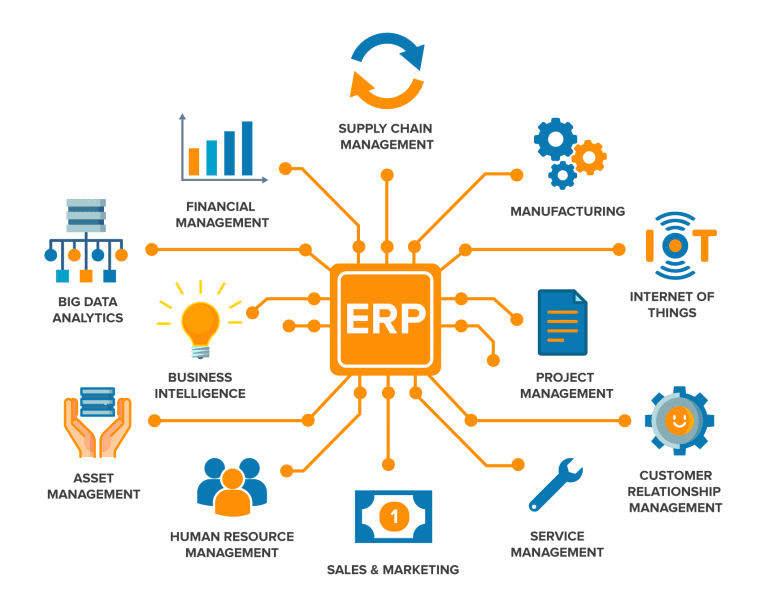
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) refers to a type of software that organizations use to manage and integrate the essential parts of their businesses. An ERP system acts as a centralized framework that brings together various business functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, customer relationship management, and more. By consolidating these processes into a single system, ERP enables better coordination, reduces redundancies, and improves overall efficiency.
The primary goal of ERP is to provide a unified view of business operations, facilitating real-time data access and enabling informed decision-making. Unlike standalone applications, ERP systems offer an integrated approach, ensuring that information flows smoothly across all departments.
Key ERP Modules
ERP systems are composed of various modules, each designed to address specific business needs. Here are some of the most common ERP modules:
1. Financial Management
This module handles all financial activities, including accounting, budgeting, forecasting, and reporting. It ensures compliance with regulatory standards and provides insights into the organization’s financial health.
2. Human Resource Management (HRM)
The HRM module manages employee-related processes such as recruitment, payroll, benefits administration, performance evaluation, and training. It helps organizations maintain a productive workforce while streamlining HR operations.
3. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
SCM focuses on the procurement of raw materials, inventory management, order processing, logistics, and supplier relationships. This module ensures that goods and services are delivered efficiently and cost-effectively.
4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
The CRM module helps businesses manage customer interactions, track sales leads, and improve customer service. It is essential for maintaining strong customer relationships and boosting sales.
5. Manufacturing
This module supports production planning, scheduling, quality control, and product lifecycle management. It ensures that manufacturing processes run smoothly and align with organizational goals.
6. Project Management
Project management modules assist in planning, executing, and monitoring projects. They help track project progress, allocate resources, and ensure timely completion.
7. Business Intelligence (BI)
BI tools within ERP systems provide advanced analytics and reporting capabilities. They transform raw data into actionable insights, helping businesses make data-driven decisions.
ERP Vendors
Several ERP vendors offer solutions tailored to different industries and business sizes. Some of the leading ERP vendors include:
1. SAP
SAP is one of the largest and most recognized ERP vendors globally. Its solutions cater to businesses of all sizes and industries, offering comprehensive modules for finance, supply chain, HR, and more.
2. Oracle
Oracle provides a wide range of ERP solutions, including cloud-based systems. Its platforms are known for scalability and advanced analytics capabilities.
3. Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 offers flexible ERP solutions that integrate seamlessly with other Microsoft products like Office 365 and Azure. It’s popular among small and medium-sized businesses.
4. Infor
Infor specializes in industry-specific ERP solutions, focusing on manufacturing, healthcare, and retail sectors. Its cloud-based offerings are designed for scalability and ease of use.
5. NetSuite
A subsidiary of Oracle, NetSuite is a cloud-based ERP solution ideal for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). It provides robust functionality across finance, CRM, e-commerce, and more.
6. Workday
Workday’s ERP solutions focus primarily on HR and financial management. Its intuitive interface and cloud-based architecture make it a preferred choice for many organizations.
Benefits of ERP in Business
Implementing an ERP system offers numerous advantages, including:
- Improved Efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks and integrating processes, ERP reduces manual effort and increases productivity.
- Better Decision-Making: Real-time data access and advanced analytics enable managers to make informed decisions quickly.
- Cost Savings: Streamlined operations and reduced redundancies lead to significant cost reductions.
- Enhanced Collaboration: A centralized database ensures that all departments have access to the same information, fostering better collaboration.
- Regulatory Compliance: ERP systems help businesses adhere to industry regulations and standards by providing built-in compliance tools.
Challenges of ERP Implementation
Despite its benefits, ERP implementation can be challenging. Common obstacles include:
- High Costs: ERP systems often require significant investment in terms of software, hardware, and training.
- Complexity: Integrating an ERP system into existing processes can be complex and time-consuming.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new systems, requiring effective change management strategies.
Conclusion
ERP systems are a critical asset for businesses aiming to enhance their operational efficiency and competitiveness. By integrating core processes and providing actionable insights, ERP solutions empower organizations to achieve their strategic objectives. While implementation requires careful planning and investment, the long-term benefits make ERP a worthwhile endeavor for businesses of all sizes and industries.













