Introduction
Parenteral nutrition (PN) is a medical technique that delivers essential nutrients directly into a patient’s bloodstream through an intravenous route, bypassing the digestive system. It is often used for patients who are unable to consume or absorb nutrients orally or enterally due to medical conditions such as gastrointestinal disorders, cancer, severe pancreatitis, or post-surgical complications. As a life-saving intervention, parenteral nutrition plays a critical role in maintaining nutritional balance, supporting recovery, and improving patient outcomes.
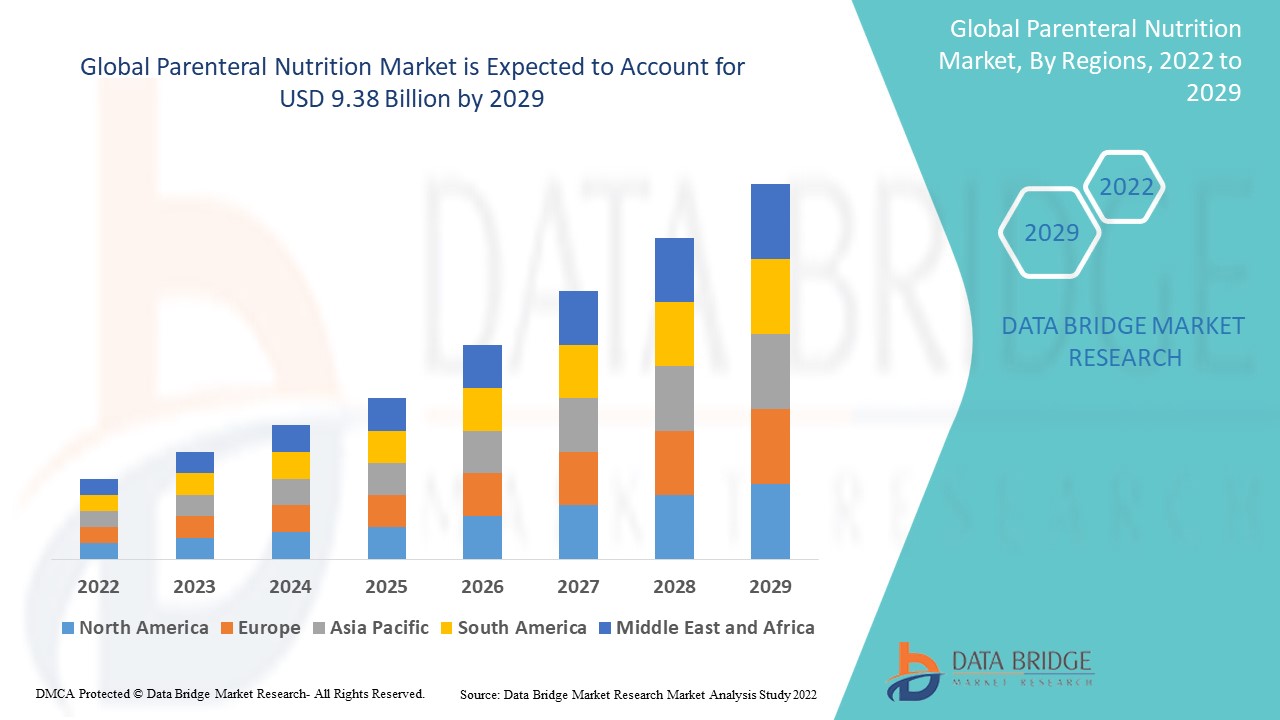
The global parenteral nutrition market is witnessing steady growth, driven by the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, premature births, advancements in healthcare infrastructure, and growing awareness about malnutrition management. Demand is also supported by an increasing elderly population that often requires nutritional support during long-term illnesses.
Source - https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-parenteral-nutrition-market
Market Overview
The parenteral nutrition market has been expanding steadily, with global revenues estimated in the multi-billion-dollar range. The market is expected to grow at a strong compound annual growth rate (CAGR) over the next decade. North America and Europe dominate due to advanced healthcare systems, but rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, supported by rising healthcare spending and higher prevalence of gastrointestinal and metabolic disorders.
Key Market Drivers
Rising Incidence of Chronic Diseases
Cancer, Crohn’s disease, short bowel syndrome, and severe gastrointestinal dysfunction are increasingly common worldwide. Patients with these conditions often require parenteral nutrition for survival and recovery.
Growth in Preterm Births
Premature infants are highly vulnerable to malnutrition due to underdeveloped digestive systems. Parenteral nutrition is essential for neonatal intensive care, driving demand in hospitals globally.
Aging Population
Elderly populations are more prone to malnutrition, chronic illnesses, and surgical procedures, increasing the use of parenteral nutrition in geriatric care.
Advancements in Formulations
Innovations in lipid emulsions, amino acid blends, and micronutrient formulations have improved the safety, efficacy, and tolerance of parenteral nutrition, encouraging adoption.
Rising Healthcare Expenditure
Improved hospital infrastructure, better reimbursement policies, and growing investments in advanced medical nutrition have further expanded access to PN therapies.
Market Challenges
Risk of Complications: Parenteral nutrition can lead to infections, liver dysfunction, or metabolic imbalances if not monitored carefully.
High Costs: PN is expensive compared to oral and enteral nutrition, which may limit access in lower-income regions.
Stringent Regulations: Stringent government regulations for manufacturing and quality control increase production costs for suppliers.
Limited Awareness: In some developing regions, lack of trained professionals and awareness about PN limits its adoption.
Market Segmentation
By Nutrient Type
Carbohydrates (Dextrose Solutions): Provide energy to critically ill patients.
Lipids (Fat Emulsions): Essential fatty acids and calorie-rich emulsions for energy balance.
Amino Acids: Critical for protein synthesis and tissue repair.
Vitamins and Minerals: Maintain metabolic functions and immunity.
Others: Electrolytes and trace elements.
By Patient Type
Pediatric and Neonatal: Premature infants and children requiring nutrition support.
Adult: Patients with chronic or critical illnesses.
By End-Use Setting
Hospitals: Primary users of PN for critical care, surgery recovery, and neonatology.
Clinics and Specialty Centers: Growing adoption in outpatient care.
Home Healthcare: Increasing demand for PN as home infusion therapies gain popularity.
Regional Insights
North America
North America leads the market due to advanced medical infrastructure, higher awareness, and growing numbers of patients with chronic diseases and cancer. The U.S. dominates the region with widespread availability of home PN services.
Europe
Europe is a mature market, with strong government support and reimbursement systems for parenteral nutrition. Germany, France, and the UK are key contributors, with rising adoption of advanced formulations.
Asia-Pacific
The fastest-growing region due to a large patient population, increasing premature births, and expanding healthcare infrastructure. China and India represent high-growth opportunities with growing investments in healthcare facilities.
Latin America
Countries like Brazil and Mexico are witnessing growth due to rising healthcare expenditure and expanding neonatal care units.
Middle East & Africa
Growth in this region is gradual but improving, supported by expanding hospital facilities and rising prevalence of malnutrition.
Competitive Landscape
The parenteral nutrition market is moderately consolidated, with multinational companies leading the industry through innovation, acquisitions, and collaborations. Key players include:
Baxter International Inc.
Fresenius Kabi AG
B. Braun Melsungen AG
Grifols S.A.
Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
Sichuan Kelun Pharmaceutical Co.
These companies focus on developing safer formulations, expanding production capacity, and strengthening distribution networks in emerging markets.
Emerging Trends
Customized Parenteral Nutrition: Growing preference for patient-specific PN formulations tailored to individual metabolic needs.
Lipid Innovations: Introduction of mixed lipid emulsions with better tolerance and fewer side effects.
Shift Toward Home Care: Increasing use of PN in home settings to reduce hospital stays and costs.
Integration of Digital Monitoring: Use of smart infusion pumps and digital platforms to monitor PN administration.
Sustainable Packaging: Rising focus on eco-friendly packaging for PN bags and components.
Future Outlook
The parenteral nutrition market is poised for strong growth over the next decade. Demand will be fueled by the increasing burden of chronic and gastrointestinal diseases, premature births, and advancements in medical nutrition formulations. Developing regions, particularly Asia-Pacific, hold immense potential as healthcare access improves.
Collaboration between pharmaceutical companies, hospitals, and research institutions will drive innovation, ensuring safer and more effective PN therapies. Home parenteral nutrition is expected to gain prominence as technology enables safe monitoring outside hospitals, aligning with cost-saving and patient convenience trends.
Conclusion
The parenteral nutrition market is an essential component of global healthcare, providing critical support for patients unable to meet their nutritional needs orally or enterally. Despite challenges such as high costs and risks of complications, the market is expanding steadily due to technological advancements, growing awareness, and rising healthcare investments. With increasing emphasis on personalized medicine and home healthcare, parenteral nutrition is set to play a more significant role in improving patient outcomes worldwide.