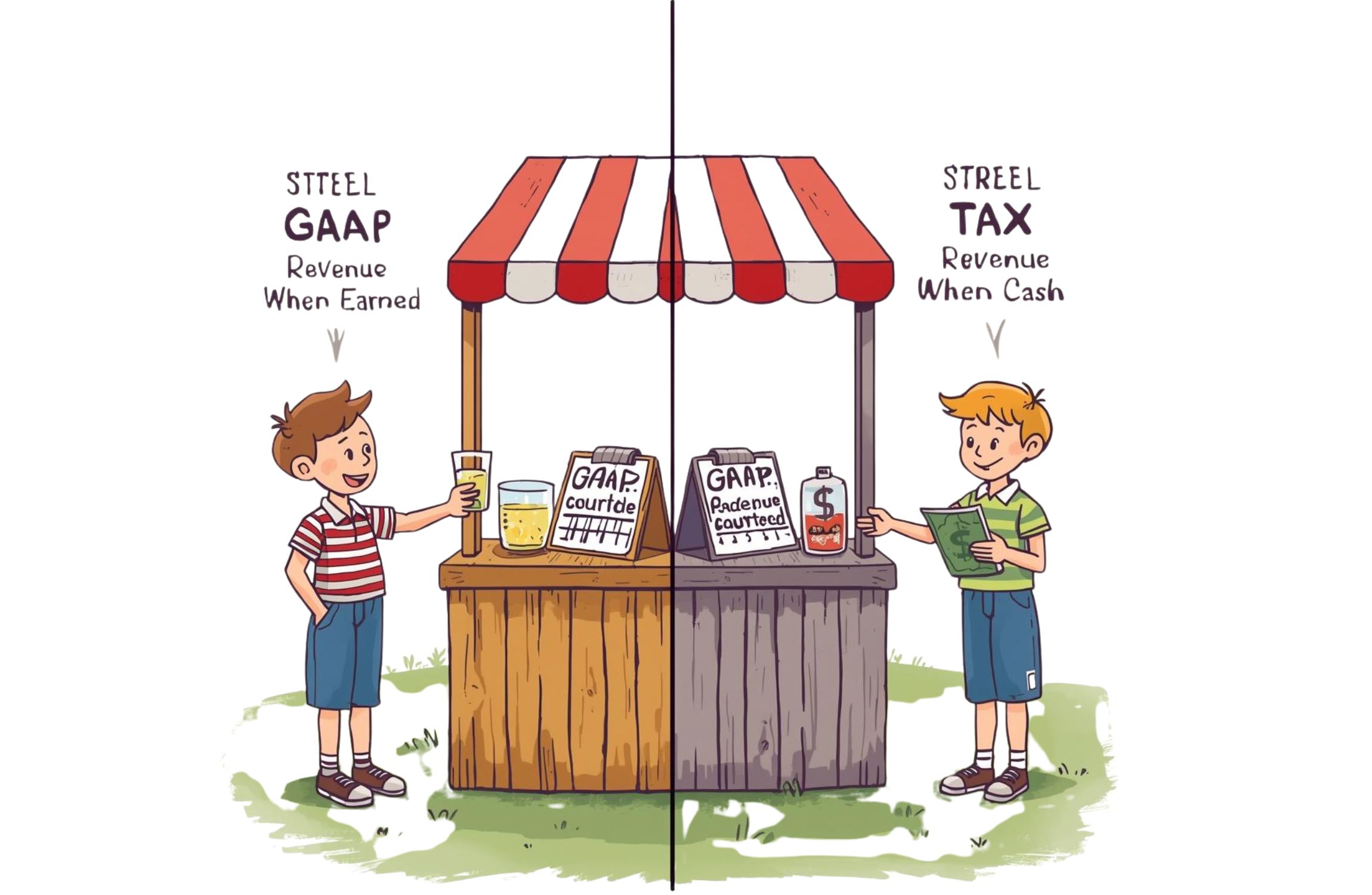
GAAP vs Tax-Basis Financial Statements: A Simple and Clear Explanation
December 13, 2025
Financial statements are one of the most important tools for running a business. They help owners understand profit, control expenses, plan for growth, and make smart decisions. However, financial statements can be prepared using different accounting methods. Two of the most common methods are GAAP and Tax-Basis financial statements.
Although both methods report income and expenses, they follow different rules and are used for different purposes. Understanding the difference can help business owners choose the right reporting method.
What Are GAAP Financial Statements?
GAAP stands for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. It is a standard set of accounting rules used in the United States. GAAP is designed to make financial statements accurate, consistent, and comparable.
Key Features of GAAP
- Uses accrual accounting
- Records income when it is earned
- Records expenses when they are incurred
- Matches expenses with related income
- Requires clear financial presentation
- Commonly required by banks and investors
GAAP financial statements show the true financial position of a business, even if cash has not yet been received or paid.
What Are Tax-Basis Financial Statements?
Tax-Basis financial statements are prepared using tax rules instead of standard accounting rules. These statements focus on how income and expenses affect taxes.
Key Features of Tax-Basis Reporting
- Often uses cash accounting
- Income is recorded when money is received
- Expenses are recorded when money is paid
- Focuses on taxable income
- Easier and faster to prepare
- Common for small and private businesses
Tax-Basis statements help business owners understand their tax responsibilities more clearly.
Main Differences Between GAAP and Tax-Basis
Purpose
- GAAP: Shows overall business performance and financial health
- Tax-Basis: Focuses on tax calculation and compliance Revenue Recognition
- GAAP: Records revenue when earned
- Tax-Basis: Records revenue when cash is receive Expense Recognition
- GAAP: Matches expenses with income
- Tax-Basis: Records expenses when paid Complexity
- GAAP: More detailed and structured
- Tax-Basis: Simple and easy to understand
Advantages of GAAP Financial Statements
- Gives a complete financial picture
- Helps with loans and investor trust
- Allows better financial analysis
- Shows long-term business performance
Disadvantages of GAAP
- More time-consuming
- Higher preparation cost
- Requires professional accounting knowledge
Advantages of Tax-Basis Financial Statements
- Simple and low-cost
- Easy for small businesses
- Directly connected to tax returns
- Less accounting complexity
Disadvantages of Tax-Basis
- Not ideal for banks or investors
- Does not show full financial performance
- Limited financial details
Which Method Is Right for Your Business?
The right method depends on your business goals.
Choose GAAP if:
- You need bank loans or investors
- You want detailed financial reporting
- You plan long-term business growth
Choose Tax-Basis if:
- Your main goal is tax reporting
- You run a small or closely held business
- You want a simple reporting system
- Some businesses use both methods for different purposes.
Final Thoughts
GAAP and Tax-Basis financial statements are both useful, but they serve different needs. GAAP provides a clear and complete view of financial performance, while Tax-Basis focuses on tax reporting and simplicity. Understanding the difference helps business owners make better financial decisions and choose the right reporting method for success.