GFA to BUA Ratio | Complete Guide for Dubai Real Estate – Regent Elite Properties
January 29, 2026
When investing in real estate or developing property in Dubai, one of the most important metrics to understand is the GFA-to-BUA ratio. Whether you are a seasoned investor, developer, or first-time buyer, knowing the difference between Gross Floor Area (GFA) and Built-Up Area (BUA), and how to calculate their ratio, is critical for evaluating property potential, regulatory compliance, and overall investment value.
At Regent Elite Properties, we aim to provide investors and property enthusiasts with clear insights into real estate metrics that matter most. This guide will help you understand:
What GFA and BUA mean
How to calculate the GFA-to-BUA ratio
Why the ratio is important in Dubai real estate
Tips for developers, investors, and buyers
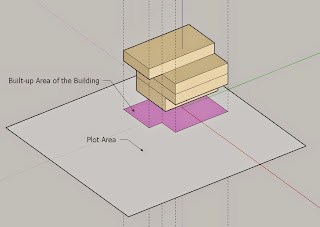
What is Gross Floor Area (GFA)?
Gross Floor Area (GFA) refers to the total floor area inside the building envelope, including all floors, basements, mezzanines, and balconies. In other words, it measures the overall size of a building from wall to wall. gfa to bua ratio
Key Points About GFA:
Includes all usable and non-usable areas (corridors, stairs, service areas)
Used by developers and planners to determine building scale
Plays a significant role in regulatory approvals and master planning
Measured in square meters (sqm) or square feet (sqft)
Example:
If a building has three floors of 200 sqm each and a basement of 100 sqm, the GFA = 200 + 200 + 200 + 100 = 700 sqm.
What is Built-Up Area (BUA)?
Built-Up Area (BUA) represents the actual constructed area that a property offers for use. It excludes common areas like hallways or service shafts and focuses on the usable space inside the property.
Key Points About BUA:
Includes bedrooms, kitchens, bathrooms, living rooms, and terraces in building
Excludes common areas, walls, and mechanical shafts
It is critical for investors to understand the livable space
Measured in sqm or sqft
Example:
A villa may have a BUA of 450 sqm while its GFA is 600 sqm due to shared corridors, balconies, and walls.
GFA vs. BUA: Understanding the Difference
| Feature | GFA | BUA |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total floor area of the building | Actual usable constructed area |
| Includes | Corridors, service areas, walls, basements | Living space, private terraces, rooms |
| Purpose | Planning, regulatory compliance | Buyer or investor understanding of usable space |
| Measured By | Architects, municipal authorities | Developers and property marketers |
Understanding this difference is crucial for investors, developers, and buyers to accurately assess property value and functionality.
What is the GFA-to-BUA ratio?
The GFA to BUA ratio is a measure that compares the gross floor area of a building to its usable built-up area. It is calculated using the formula:
GFA to BUA Ratio = Gross Floor Area (GFA) Built-Up Area (BUA)\text{GFA to BUA Ratio} = \frac{\text{Gross Floor Area (GFA)}} {\text{Built-Up Area (BUA)}} GFA to BUA Ratio = Built-Up Area (BUA) / Gross Floor Area (GFA)
Example Calculation:
If a villa has
GFA = 600 sqm
BUA = 450 sqm
GFA to BUA Ratio=600450=1.33\text{GFA to BUA Ratio} = \frac{600}{450} = 1.33GFA to BUA Ratio=450600=1.33
This means that for every 1.33 sqm of total building area, only 1 sqm is usable space.
Importance of GFA to BUA Ratio in Real Estate
The GFA-to-BUA ratio is crucial for developers, investors, and buyers for several reasons:
1. Determines Property Efficiency
A lower GFA-to-BUA ratio indicates that more of the building is usable space, which is preferable for residential or commercial purposes.
2. Impacts Property Value
Investors often consider the BUA because it represents the actual usable area. Properties with a higher BUA relative to GFA are typically more valuable.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Dubai’s Dubai Land Department (DLD) and other authorities may use GFA in approvals for zoning, building permits, and density regulations.
4. Guides Developers in Design
Architects and developers use this ratio to optimize space for residents while complying with regulations.
5. Aids Buyer Decisions
Buyers can evaluate whether a property offers adequate living space compared to the total built area, ensuring a fair investment.
Factors Affecting GFA to BUA Ratio
Several factors influence this ratio in real estate projects:
1. Building Design
Multi-story vs. single-story
Floor layouts and mezzanines
2. Common Areas
Hallways, staircases, lobbies, and service areas increase GFA without increasing BUA
3. Architectural Features
Balconies, terraces, and atriums may add to GFA but not always to usable BUA
4. Regulatory Requirements
Minimum setback distances and parking requirements can affect the ratio
5. Construction Quality
Wall thickness, material choices, and space utilization affect the efficiency of usable space
Ideal GFA to BUA Ratio
While the ideal ratio depends on property type, location, and developer priorities:
Residential villas and apartments: 1.2–1.4
Commercial buildings: 1.3 – 1.5
Luxury developments: May vary depending on design aesthetics
A lower ratio is generally better, indicating efficient use of space and a higher livable area.
How Investors Use the GFA-to-BUA Ratio
Investors in Dubai’s real estate market consider the GFA-to-BUA ratio for:
1. Pricing Decisions
Higher BUA relative to GFA may justify a higher price per square foot, offering better returns.
2. Rental Income Evaluation
More usable space typically translates to higher rental potential.
3. Long-Term Value
Efficient space planning ensures sustainable property appreciation.
4. Comparing Properties
Investors can compare different developments on a like-for-like basis using this ratio to determine value efficiency.
GFA to BUA Ratio in Dubai Real Estate Regulations
Dubai has specific building and planning regulations that impact GFA and BUA:
Zoning and FAR (Floor Area Ratio): Determines maximum allowable GFA for a plot
Setback requirements: Affect total buildable area
DLD rules: Ensure transparent registration and compliance with density regulations
Developers must carefully calculate GFA-to-BUA ratios to ensure legal compliance and optimize property value.
Tips for Developers and Buyers
For Developers:
Optimize floor layouts to maximize BUA
Minimize non-usable areas like excessive corridors
Use modern construction techniques for thinner walls and better space efficiency
For Buyers:
Always ask for both GFA and BUA details
Compare ratios across similar properties
Consider the ratio in relation to your budget and lifestyle needs
Why Choose Regent Elite Properties for Dubai Real Estate
At Regent Elite Properties, we help investors and buyers navigate complex real estate metrics like GFA, BUA, and their ratios. Our services include:
Accurate property evaluations
Guidance on GFA to BUA efficiency
Investment advice for high-value properties
Transparent market insights
With our expertise, you can make informed decisions and maximize your returns in Dubai’s competitive property market.
Conclusion
The GFA-to-BUA ratio is more than a technical metric—it is a critical tool for property valuation, investment analysis, and development planning. Understanding this ratio helps investors, developers, and buyers make better decisions, ensure regulatory compliance, and evaluate property efficiency.
For anyone looking to invest in or develop property in Dubai, knowing the difference between GFA and BUA and using their ratio to compare properties is essential. With Regent Elite Properties, you gain expert guidance and market insights to make profitable and informed real estate decisions.
You Might Like Also
Architects in Islamabad

Shop Bras Online in Pakistan at Mussarat Lingerie