Venous leak, medically referred to as venogenic erectile dysfunction, is a condition that primarily affects men and can significantly impact sexual health and quality of life. Though often misunderstood, venous leak is a well-recognized medical condition where the veins in the penis fail to trap and maintain blood during an erection, leading to difficulty in achieving or sustaining erections suitable for sexual activity.
This article delves deep into venous leak, explaining its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and preventive strategies, providing a complete resource for patients and caregivers alike.
What is Venous Leak?
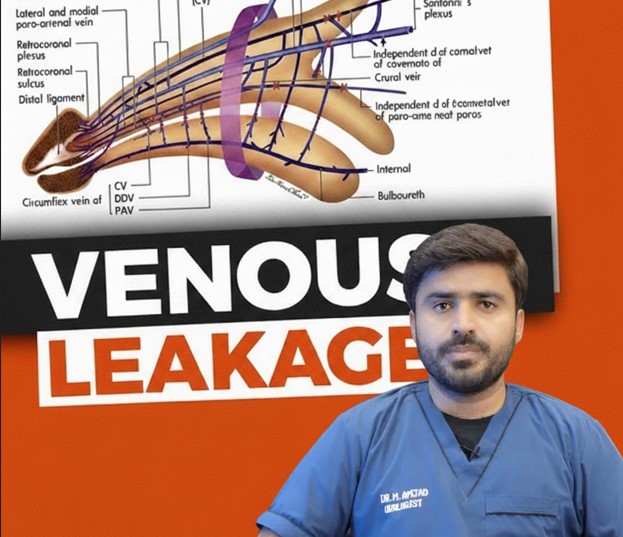
The human penis relies on a complex interaction between arteries, veins, and erectile tissue to achieve and maintain an erection. During sexual arousal, arteries in the penis expand, increasing blood flow into the corpora cavernosa, two sponge-like chambers in the penis. Normally, veins compress to trap this blood inside the corpora cavernosa, resulting in a firm and sustained erection.
A venous leak occurs when the veins fail to constrict adequately. This inability to retain blood in the corpora cavernosa causes the erection to be soft, unstable, or short-lived, even with sufficient sexual stimulation. Essentially, blood "leaks" out of the penis faster than it should, leading to erectile dysfunction (ED).
Venous leak is sometimes referred to as venogenic erectile dysfunction because the underlying problem originates in the veins rather than in hormonal or neurological systems.
Causes of Venous Leak
Venous leak can result from multiple factors, including structural, physiological, and lifestyle-related issues. Some of the common causes include:
1. Age-Related Changes
As men age, the elasticity of penile tissue and veins may decrease, impairing the ability of veins to trap blood effectively. While venous leak can occur in younger men, age increases the risk significantly.
2. Trauma or Injury
Physical trauma to the penis or pelvic region can damage the veins or connective tissue in the corpora cavernosa, resulting in a venous leak. Sports injuries, accidents, or surgical complications can contribute to this condition.
3. Connective Tissue Disorders
Some men have weakened connective tissues in the penis, either due to genetic factors or acquired conditions, which prevents the veins from compressing efficiently. Disorders like Peyronie’s disease, which causes abnormal fibrous tissue formation in the penis, may also lead to venous leak.
4. Cardiovascular Diseases
Since erectile function depends heavily on blood flow, conditions like atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, or diabetes can damage blood vessels and contribute to venous leak.
5. Hormonal Imbalances
Although less common, low testosterone levels or other hormonal disruptions can indirectly contribute to venous leak by affecting overall erectile function.
6. Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, alcohol abuse, sedentary lifestyle, and poor diet can damage vascular health and exacerbate venous leak. Men with these risk factors are more prone to developing erectile dysfunction, including venous leak.
Symptoms of Venous Leak
Identifying venous leak early is crucial for effective treatment. The symptoms may vary but commonly include:
Inability to Achieve a Firm Erection – Despite sexual arousal, the penis does not become sufficiently rigid.
Erections that Lose Firmness Quickly – An erection may start strong but diminish rapidly.
Softening During Intercourse – Loss of rigidity often occurs mid-activity, affecting sexual satisfaction.
Reduced Penile Rigidity Despite Morning Erections – Men with venous leak may notice that morning erections are less firm or shorter than before.
Decreased Sexual Confidence – Recurrent erectile issues can cause psychological distress, anxiety, or depression.
It is important to note that venous leak is often progressive, meaning that untreated cases may worsen over time.
Diagnosing Venous Leak
Diagnosis of venous leak involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and specialized imaging studies.
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
A urologist will review the patient’s sexual history, lifestyle factors, and overall health. Physical examination may involve checking penile anatomy, vascular health, and neurological function.
2. Blood Tests
Hormone levels, including testosterone, prolactin, and thyroid function tests, may be evaluated to rule out hormonal causes of erectile dysfunction.
3. Penile Doppler Ultrasound
Penile Doppler ultrasound is one of the most common diagnostic tools. It measures blood flow in the arteries and veins of the penis and helps detect whether blood is escaping through the veins prematurely.
4. Cavernosometry and Cavernosography
These advanced procedures provide detailed information about the veins and the venous leak:
Cavernosometry: Measures intracavernosal pressure during an erection induced by medication.
Cavernosography: Involves injecting contrast material into the penis to visualize veins and pinpoint areas of leakage using X-ray imaging.
5. Nocturnal Penile Tumescence Test
This test evaluates erections that occur during sleep. Men with venous leak may still achieve normal nocturnal erections, helping distinguish venous causes from neurological or hormonal causes of erectile dysfunction.
Treatment Options for Venous Leak
Treatment for venous leak depends on the severity, underlying cause, and patient preferences. Approaches range from lifestyle modifications and medications to minimally invasive procedures and surgery.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Improving cardiovascular health can positively affect erectile function:
Exercise regularly to improve blood circulation.
Quit smoking and reduce alcohol consumption to protect vascular health.
Maintain a healthy weight to prevent comorbidities like diabetes and high blood pressure.
Balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support vascular function.
2. Medications
Oral medications like phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5 inhibitors) — sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) — improve blood flow to the penis.
However, men with severe venous leak may not respond adequately to medications alone, as these drugs primarily enhance arterial inflow, not venous trapping.
3. Vacuum Erection Devices
A vacuum erection device (VED) creates negative pressure around the penis to draw blood into the corpora cavernosa. A constriction ring placed at the base of the penis helps maintain the erection by preventing venous outflow temporarily.
4. Penile Injections
Intracavernosal injections of vasodilators such as alprostadil, papaverine, or phentolamine directly relax penile smooth muscle, enhancing blood inflow and sometimes compensating for venous leakage.
5. Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered for men who do not respond to conservative treatments:
a. Venous Ligation Surgery
This involves tying off or sealing veins that are leaking blood. Success rates vary, and surgery is most effective in younger men with isolated venous leaks.
b. Penile Prosthesis Implantation
For severe or refractory cases, penile implants — either inflatable or semi-rigid — provide a permanent solution by mechanically creating erections. This approach bypasses venous leak entirely.
Complications of Untreated Venous Leak
If left untreated, venous leak can cause:
Persistent erectile dysfunction
Psychological effects such as anxiety, depression, or reduced self-esteem
Relationship difficulties
Reduced sexual satisfaction
Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent long-term complications and restore sexual function effectively.
Preventive Measures
While not all cases of venous leak can be prevented, certain strategies may reduce risk:
Maintain cardiovascular health through regular exercise and a healthy diet.
Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Manage chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol.
Seek timely medical care after penile trauma or injuries.
Address erectile issues early rather than delaying treatment.
Prognosis
The prognosis of venous leak depends on the cause, age, and treatment approach. Young men with isolated venous leak who undergo surgical repair often have favorable outcomes. Older men or those with comorbid conditions may benefit more from combination therapies, including medications, vacuum devices, or implants.
With appropriate management, men with venous leak can regain functional erections and maintain sexual health.
FAQs About Venous Leak
1. Can venous leak be reversed without surgery?
Yes, mild cases may respond to lifestyle changes, medications, and vacuum devices. However, severe leaks may require surgical intervention for long-term correction.
2. Is venous leak common?
Venous leak is a recognized cause of erectile dysfunction but is less common than other forms of ED such as those caused by diabetes, hypertension, or psychological factors.
3. Can young men develop venous leak?
Yes, although it is more common with age, young men may develop venous leak due to trauma, connective tissue disorders, or congenital vascular abnormalities.
4. Does venous leak affect fertility?
Venous leak primarily affects erections and sexual function, not sperm production or fertility directly. However, sexual dysfunction may indirectly affect reproductive outcomes.
5. Are penile implants safe for venous leak?
Yes, modern penile implants are highly effective and safe, providing a permanent solution for men who do not respond to other treatments.
Conclusion
Venous leak is a significant cause of erectile dysfunction that can impact quality of life and psychological well-being. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for early diagnosis and effective management.
From lifestyle interventions and medications to advanced surgical procedures, multiple strategies exist to manage venous leak and restore sexual function. Men experiencing difficulty maintaining erections should consult a qualified urologist promptly, as early intervention increases the likelihood of successful treatment and improved sexual health.
With proper care, education, and medical guidance, venous leak is a manageable condition, allowing men to regain confidence, intimacy, and overall well-being.