Introduction
There’s a familiar moment in many businesses when data collection shifts from manageable to why is this taking so long? It usually happens quietly during a rushed report a missed insight, or a dataset that suddenly stops updating. That moment often marks the first real encounter with the limits of traditional scraping methods. As companies grow more dependent on timely information, the way data is gathered becomes a strategic concern rather than a technical footnote. This is where the comparison between web scraping and traditional scraping truly matters. Understanding how each approach works, where it excels, and where it falls short can save businesses time, resources, and unnecessary frustration. Before tools are chosen or systems are built, it helps to step back and examine what’s really happening beneath the surface of data collection.
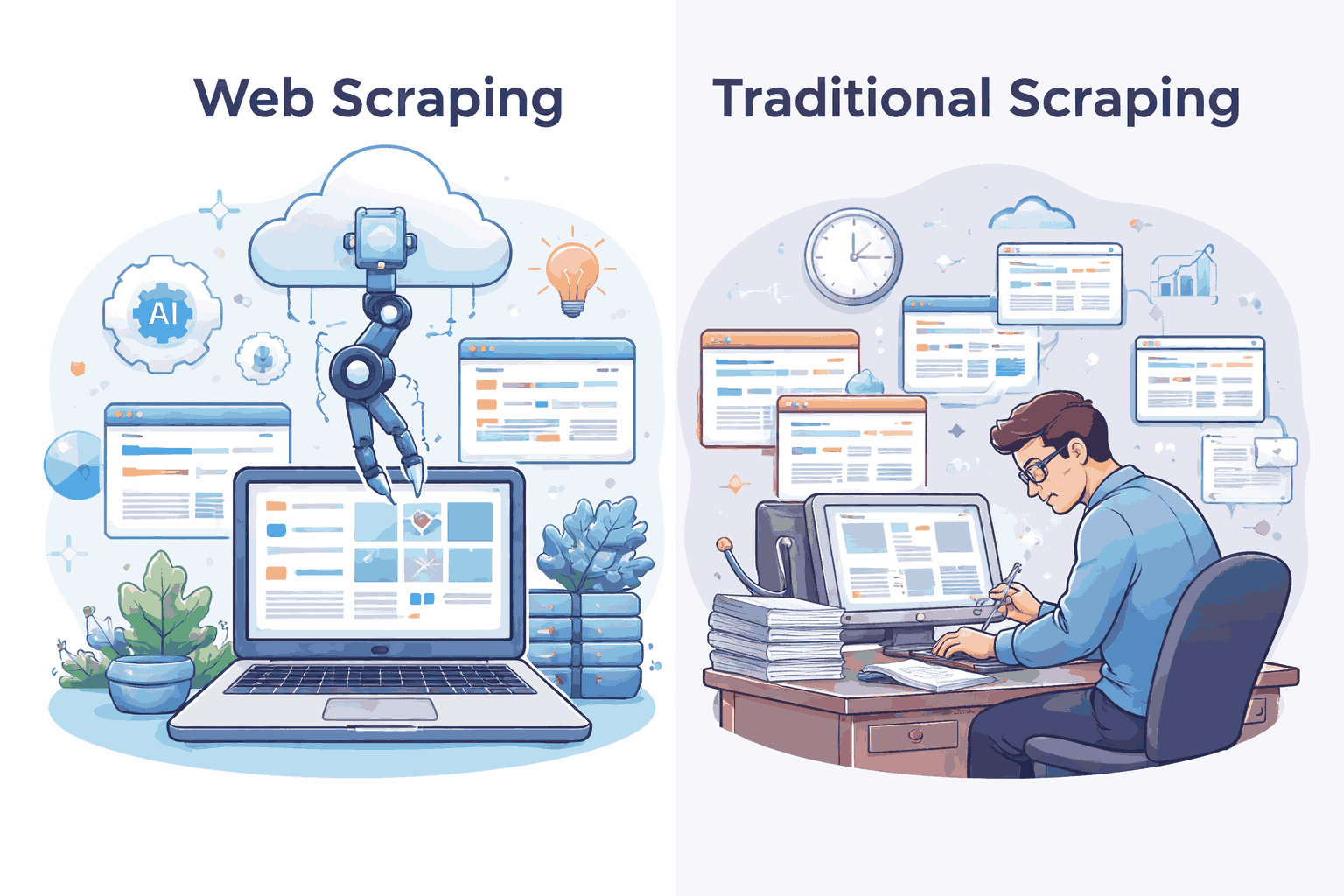
What Is Traditional Scraping?
Traditional scraping is the “we’ve always done it this way” method of data collection. It often relies on rigid scripts, manual downloads, or static tools that pull information from predictable sources. Think legacy systems, fixed HTML structures, and a lot of babysitting. When it works, it feels efficient. When a website layout changes (which it always does), everything breaks—quietly, usually on a Friday afternoon. Businesses once tolerated this because options were limited and data needs were smaller. But traditional scraping struggles with scale, flexibility, and accuracy. There’s also the hidden cost: time. Engineers maintaining brittle scripts instead of building products. Which leads us, quite naturally, to the newer, more adaptable alternative—because frustration is a powerful driver of innovation.
What Is Web Scraping?
Web scraping is traditional scraping’s more adaptable, better-dressed cousin. Instead of relying on fragile rules, modern solutions are built to handle dynamic websites, large data volumes, and frequent changes without constant human intervention. This is where web scraping services shine—offering scalable infrastructure, automated maintenance, and cleaner outputs. Businesses can collect data in near real time, across thousands of sources, without holding their breath every time a website updates its layout. (Progress is beautiful.) The real difference, though, is mindset: web scraping treats data collection as an ongoing system, not a one-off task. And once you experience that shift, going back to manual or legacy methods feels a bit like choosing a fax machine over email—technically possible, but emotionally exhausting.
Key Differences: Web Scraping vs Traditional Scraping
At a glance, both approaches extract information. Dig a little deeper, and the contrast becomes stark. Traditional scraping is slower, more fragile, and heavily dependent on constant maintenance. Web scraping prioritizes automation, resilience, and scale. Accuracy improves because systems adapt instead of failing silently. Costs also differ—traditional methods may look cheaper upfront, but hidden labor and downtime add up quickly. Web scraping solutions are designed to grow with your business, not fight it. There’s also compliance to consider: modern tools often include safeguards that older scripts simply ignore. In short, one approach is reactive, the other proactive. And businesses that rely on timely data usually learn—sometimes the hard way—that proactive wins.
The Role of AI in Modern Data Collection
This is where things get interesting. Ai data scraping introduces intelligence into what was once a very mechanical process. AI can recognize patterns, adapt to layout changes, and identify relevant data even when structures shift. Instead of breaking, systems learn. For businesses, this means higher accuracy, less downtime, and far fewer “why is this column empty?” meetings. AI also helps filter noise, delivering cleaner, more relevant datasets. I like to think of it as finally giving the machines the boring work they deserve—while humans focus on decisions, not debugging. Naturally, this evolution didn’t happen for fun. It happened because companies demanded faster insights and less operational pain. And AI was more than happy to oblige.
Business Use Cases: When Each Approach Makes Sense
Not every business needs the same solution—context matters. Traditional scraping can still work for small, static projects with limited scope and zero tolerance for subscription costs. But as soon as you scale—multiple sources, frequent updates, competitive monitoring—web scraping becomes the sensible choice. E-commerce teams track pricing, startups validate markets, analysts monitor trends, and sales teams enrich leads. All of these depend on timely, reliable data. The larger the operation, the more painful outdated methods become. I’ve noticed a pattern: companies rarely upgrade scraping tools because they want to—they do it because growth makes inefficiency impossible to ignore. Growth has a way of exposing technical shortcuts.
Data Quality, Compliance, and Risk
Collecting data is easy; collecting usable data is not. Poor data quality leads to bad decisions, and bad decisions have expensive consequences. Modern scraping focuses heavily on structured, validated data Extraction, reducing duplicates, errors, and inconsistencies. Compliance is another critical factor—especially with evolving data regulations. Legacy scraping methods often ignore legal nuance, creating unnecessary risk. Today’s solutions are built with governance in mind, helping businesses stay on the right side of regulations without constant legal firefighting. The irony? Companies often worry about scraping risks while relying on outdated tools that create more exposure than protection. Clean data isn’t just a technical win—it’s a strategic safeguard.
How Businesses Should Choose the Right Approach
Choosing between approaches starts with asking better questions. How often does the data change? How critical is accuracy? What happens if the pipeline fails for a day—or a week? Businesses should evaluate total cost, not just licensing fees. Maintenance time, downtime, and missed opportunities matter. Scalability matters even more. The smartest teams think long-term, aligning data strategy with growth goals instead of short-term convenience. I’ve seen companies delay this decision for months, only to rush it later under pressure. (Pressure is a terrible project manager.) A deliberate choice now almost always beats an emergency upgrade later.
Future of Scraping for Businesses
The future of scraping is quieter, smarter, and far more automated. AI-driven systems will continue to reduce human intervention, adapt faster, and deliver insights closer to real time. Traditional scraping won’t vanish overnight, but it will increasingly feel like legacy infrastructure—functional, but limiting. Businesses that treat data as a strategic asset will invest accordingly. Those that don’t will keep wondering why competitors move faster with fewer people. Progress rarely announces itself loudly; it just makes old methods feel inconvenient. And inconvenience, as history shows, is usually the first sign that change is overdue.
Conclusion
If there’s one thing I’ve learned—from spreadsheets, scripts, and too many “quick fixes”—it’s that data collection should make your business smarter, not more stressed. Traditional scraping had its moment, and it served its purpose. But today’s pace demands systems that adapt, scale, and quietly do their job without drama. The real choice isn’t between tools; it’s between reacting to problems and designing around them. Businesses that choose thoughtfully don’t just collect data—they trust it. And trust, in a data-driven world, is worth far more than another brittle script held together by hope and comments from 2017.
FAQs
What is the main difference between web scraping and traditional scraping?
The main difference lies in adaptability and scale. Web scraping is automated and resilient, while traditional scraping is rigid and maintenance-heavy.
Is web scraping legal for businesses?
Yes, when done responsibly. Businesses must respect website terms, public data rules, and applicable regulations.
How does AI improve scraping accuracy?
AI adapts to changing layouts, identifies relevant patterns, and reduces errors caused by structural changes.
Which industries benefit most from scraping technologies?
E-commerce, finance, marketing, real estate, and SaaS companies benefit heavily from timely data access.
Can small businesses use scraping effectively?
Absolutely. Scalable tools allow small teams to access enterprise-level data without heavy infrastructure.