
Machine guarding refers to the safety measures and physical barriers put in place to protect workers from the hazards associated with machinery and equipment in industrial settings. The primary purpose of machine guarding is to prevent accidental contact with moving parts, electrical components, or other dangerous elements of machinery that could cause injury or harm.
Here are some common types of machine guarding:
Fixed Guards: These are permanent physical barriers that enclose the hazardous parts of machinery, such as blades, gears, or belts. Fixed guards are securely attached to the machine frame and prevent access to the danger zone while the machine is in operation.
Interlocking Guards: Interlocking guards are designed to disable the machine or interrupt its operation if the guard is opened or removed. They use sensors or switches to detect when the guard is not in place, ensuring that the machine cannot be operated without proper guarding.
Adjustable Guards: Adjustable guards can be moved or repositioned to accommodate different sizes of materials or workpieces while still providing protection from the machine's moving parts. These guards are often used in conjunction with various types of machinery
You Might Like Also

chain belt drive guard
pump coupling safety guard

bench grinder machine safety guard
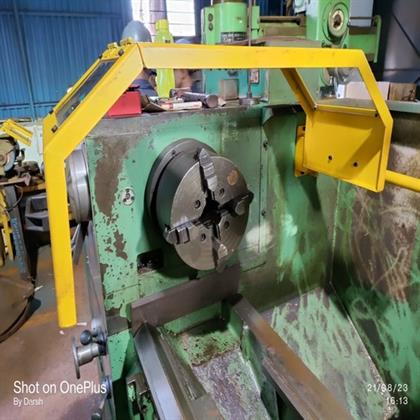

Lathe machine safety guard

safety guards

drilling machine safety guard













